Difference Between Bacteria and Virus
Microorganisms, also called microbes, are present everywhere around us. Some of these microbes are useful for humans, while others can cause harmful diseases. Among all microbes, bacteria and viruses play the biggest role in causing infections and illnesses. Bacteria can be both helpful and harmful, but viruses are mostly responsible for serious and dangerous diseases. Because these two microorganisms affect human life so much, it is very important to understand what bacteria and viruses are, where they are found, how they live, and how they are different from each other.
What Are Bacteria
Bacteria are considered the first living organisms on Earth. Scientists believe that bacteria have been present on Earth for almost three billion years. The scientific study of bacteria is called bacteriology. Bacteria are unicellular organisms, which means they are made of only one cell. All important life functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction happen inside this single cell.
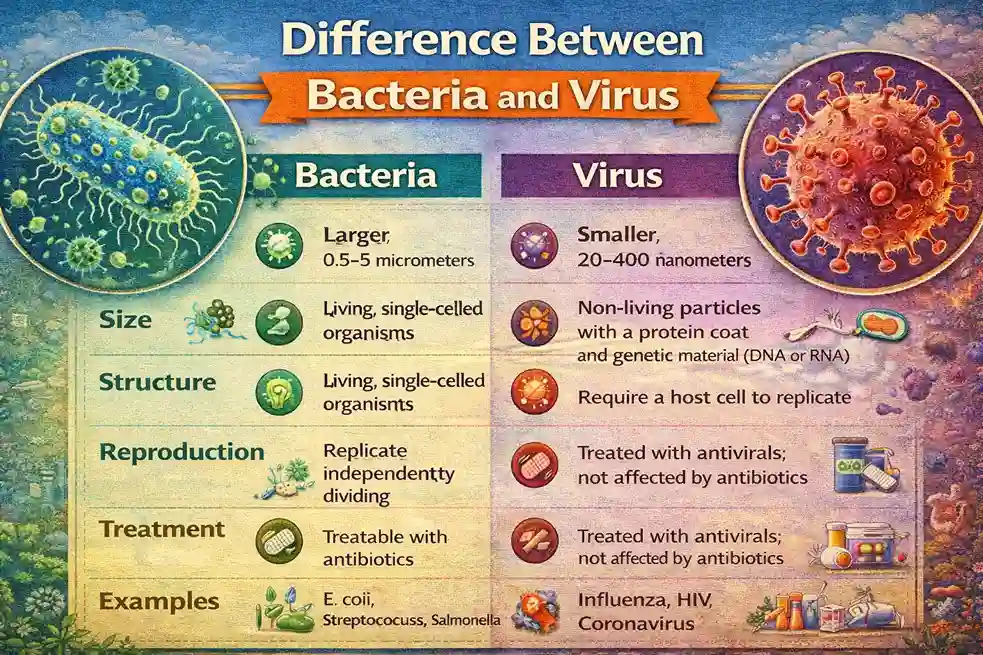
A bacterial cell has a cell wall, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. Bacteria are smaller than eukaryotic cells but larger than viruses. The size of bacteria usually ranges from 0.5 to 5 micrometers. Even though bacteria are very small, they exist in huge numbers and can survive in almost every environment on Earth.
Bacteria are found in soil, oceans, rivers, deserts, snow, air, and even inside the human body. In the human gut, bacteria help in digestion and support the immune system. They are also present in animals and often live in a symbiotic relationship with fungi and other organisms. It is estimated that one teaspoon of fertile soil contains more than 500 million bacteria. Surprisingly, the number of bacteria present in the human mouth is more than the total number of humans on Earth.
Shapes and Types of Bacteria
Bacteria are found in different shapes. There are three basic bacterial shapes. Spherical or ball-shaped bacteria are called cocci. Rod-shaped bacteria are known as bacilli. Spiral or helical-shaped bacteria are called spirochetes.
Based on cell wall structure, bacteria are divided into two main types: gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have thick cell walls, while gram-negative bacteria have thin cell walls. For example, Staphylococcus is gram-positive, while Vibrio cholerae is gram-negative.
Based on nutrition, bacteria are classified into autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria. Autotrophic bacteria can make their own food, such as cyanobacteria and Rhodospirillum. Heterotrophic bacteria cannot make their own food and depend on other organisms or dead organic matter, such as Salmonella and Agrobacterium.
Based on respiration, bacteria are divided into aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria need oxygen to produce energy, such as Lactobacillus and Nocardia. Anaerobic bacteria can survive without oxygen, such as Bacteroides.
What Are Viruses
Viruses are microscopic organisms that are responsible for many diseases around the world. The study of viruses is called virology. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and are found in different sizes. Most viruses range between 20 to 400 nanometers. They are about 100 to 1000 times smaller than human body cells.
Viruses are not considered completely living organisms because they cannot perform life functions on their own. They cannot convert food into energy, cannot respire, and cannot excrete waste. However, viruses can reproduce, but only inside a host cell. Because of this unique nature, viruses are often considered a link between living and non-living things.
Viruses do not have a proper cell wall. Instead, they have a protective protein layer that surrounds their genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA. Viruses do not have their own metabolic system. Once they enter a host cell, they take control of the host’s metabolic activities and use the host’s resources to reproduce.
Shapes and Types of Viruses
Viruses are mainly found in three shapes. Some viruses are bullet-shaped, such as the rabies virus. Some are filament-shaped, like the Ebola virus. Others are brick-shaped or oval-shaped, such as the pox virus.
Based on the type of host they infect, viruses are divided into animal viruses, plant viruses, and bacteriophages. Animal viruses infect humans and animals and cause diseases like influenza, rabies, mumps, polio, and COVID-19. Plant viruses infect plants and reduce crop production, such as tobacco mosaic virus, potato virus, and beet yellow virus. Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacterial cells. An example is the T4 bacteriophage, which infects Escherichia coli bacteria.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteria and viruses are responsible for many infectious diseases. Bacterial infections include sore throat, food poisoning, tuberculosis, cholera, meningitis, urinary tract infections, syphilis, gonorrhea, and Lyme disease.
Viral infections include influenza, common cold, measles, mumps, rubella, polio, rabies, COVID-19, chickenpox, and HIV. Most bacterial and viral diseases are different, but their methods of spreading are often similar.
How Bacterial and Viral Infections Spread
Both bacterial and viral infections can spread through coughing and sneezing, close contact with an infected person, touching contaminated surfaces, contact with infected animals or insects, and transmission from mother to child during birth. Because their modes of transmission are similar, preventive measures like hygiene and vaccination are very important.
Treatment and Prevention
Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics. Viral infections are treated using antiviral medicines, although many viral infections mainly require supportive care. Compared to bacterial infections, more vaccines are available for viral diseases. Vaccines exist for hepatitis A, hepatitis B, influenza, rabies, polio, measles, mumps, and rubella, among others.
Major Differences Between Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteria are single-celled living organisms that can survive independently, while viruses are much smaller and can survive only inside a host cell. Bacteria are found in almost every environment, while viruses have limited survival outside a host. Bacteria contain only DNA, while viruses can contain either DNA or RNA.
Only a small percentage of bacteria are harmful to humans, while most viruses cause diseases. Bacteria have a cell wall, but viruses do not. Bacteria can survive for long periods in the environment, whereas viruses survive only for a short time outside a host. Bacterial diseases usually have a longer incubation period, while viral diseases often show symptoms quickly.
Conclusion
Bacteria and viruses are two important types of microorganisms that affect human life in many ways. While bacteria can be both helpful and harmful, viruses are mainly disease-causing agents. They differ in size, structure, survival, reproduction, and treatment methods. Understanding these differences helps us take better preventive measures, follow correct treatments, and protect ourselves from infections. Proper knowledge about bacteria and viruses is essential because humans encounter them throughout life, and awareness is the first step toward good health.
