Greenhouse Effect: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions
You may have heard or read about the greenhouse effect many times, but have you ever seen a real greenhouse? A greenhouse is a structure made of glass walls and a glass roof. Inside it, plants like tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and lettuce are grown. It is designed in a special way so that heat from the sun enters easily but cannot escape. Because of this, the inside temperature stays warm, which helps plants grow even in cold weather.
Glass traps heat very effectively. That is why greenhouses remain warm even during freezing winters. This simple and smart idea helps farmers grow plants in cold regions. Interestingly, something very similar happens around our planet Earth. This natural process is called the greenhouse effect.
What Is the Greenhouse Effect?
When sunlight reaches the Earth, it passes through the atmosphere and warms the Earth’s surface. The Earth then releases some of this heat back into the atmosphere, especially during the night. However, gases present in the atmosphere trap part of this heat and stop it from escaping completely into space.
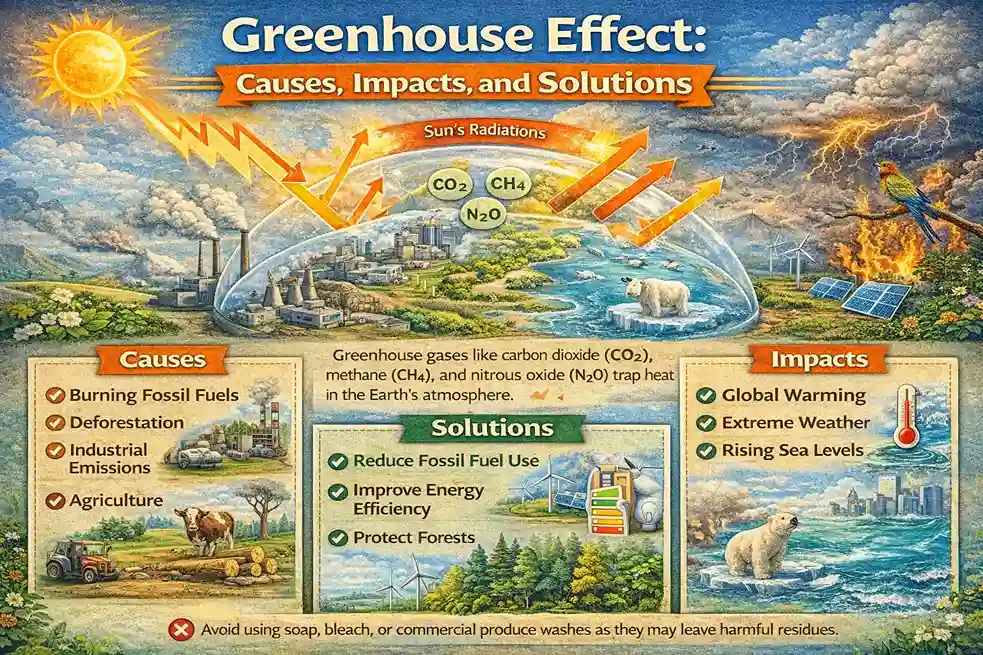
These gases act like a blanket around the Earth. Because of them, the planet stays warm enough to support life. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor.
Due to this natural greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the Earth stays around 15 degrees Celsius. This temperature is perfect for plants, animals, and humans to survive. Without this natural process, the Earth would be extremely cold, with an average temperature around minus 18 to minus 20 degrees Celsius. In such conditions, normal life would not be possible.
So, the natural greenhouse effect is not bad. In fact, it is essential for life on Earth. The real problem starts when human activities disturb this natural balance.
Greenhouse Gases and Their Role
Greenhouse gases are very good at trapping heat. Carbon dioxide is one of the most important greenhouse gases. It is released naturally through volcanic activity, plant respiration, and breathing by animals and humans. However, after the industrial revolution, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased rapidly.
Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas for electricity, transport, and industries releases large amounts of carbon dioxide. Deforestation also increases carbon dioxide levels because trees that absorb this gas are cut down. Today, carbon dioxide levels are about 50 percent higher than they were in the past.
Methane is another powerful greenhouse gas. It is naturally produced during the decomposition of organic matter. But human activities have greatly increased methane emissions. Cattle farming, rice farming, oil and gas production, and waste disposal sites release large amounts of methane into the atmosphere.
Nitrous oxide is also a dangerous greenhouse gas. It is released through the use of chemical and organic fertilizers, burning of fossil fuels, and biomass burning. Even though it is present in smaller amounts, it traps heat very effectively.
Water vapor plays an important role too. As the Earth warms, more water evaporates into the atmosphere. Water vapor then traps even more heat, which increases warming further.
Man-Made Greenhouse Gases
Apart from natural gases, humans have created some greenhouse gases during industrial processes. These include hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride. These gases are present in very small amounts, but they are extremely powerful at trapping heat. Even a small increase in their concentration can cause serious warming.
Global Warming and Its Effects
Because of the increasing amount of greenhouse gases, the Earth’s surface temperature is rising rapidly. This rise in average temperature is called global warming. Today, global warming has become a serious problem. If strong actions are not taken, it could threaten life on Earth.
Rising temperatures have damaged the ozone layer, which protects us from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays. As a result, more UV rays are reaching the Earth, increasing the risk of skin cancer and other health problems.
Air pollution and smog have also become common. Vehicles, industries, agricultural fires, and forest fires release harmful gases and smoke into the air. These pollutants not only harm human health but also add to the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse gases also mix with rainwater and cause acid rain. Acid rain damages soil, crops, forests, and water bodies. Oceans absorb a large amount of carbon dioxide, which makes them acidic. This acidic water harms coral reefs, shellfish, and other marine life.
Runaway Greenhouse Effect and the Lesson from Venus
To understand how dangerous this situation can become, we need to look at the runaway greenhouse effect. This process once happened on the planet Venus.
Billions of years ago, Venus had a temperature between 20 and 50 degrees Celsius, which could support life. It even had liquid water oceans. Over time, more water vapor entered its atmosphere. Water vapor trapped more heat, which increased the planet’s temperature. Higher temperature caused even more water to evaporate, creating a feedback cycle.
Eventually, all water on Venus turned into vapor and escaped. Carbon dioxide levels increased, trapping even more heat. Today, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system, even hotter than Mercury, despite being farther from the sun.
Scientists warn that if greenhouse gases continue to increase on Earth, a similar runaway greenhouse effect could happen here too. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, and melting glaciers are already warning signs.
What Can Humans Do to Reduce the Greenhouse Effect?
The good news is that humans can still take action. Governments, industries, and individuals all have an important role to play. One major global effort was the Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1997 and implemented in 2005. Its goal was to reduce industrial greenhouse gas emissions.
At an individual and community level, many steps can be taken. Deforestation should be stopped, and more trees should be planted to absorb carbon dioxide. Fuel efficiency of vehicles should be improved, and electric or zero-emission vehicles should be promoted.
Alternative energy sources like solar power, wind energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy, biomass energy, and hydropower should be used more. These renewable sources do not burn fossil fuels and do not release greenhouse gases.
In farming, the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers should be reduced. Energy-efficient appliances should be chosen, and their energy ratings should be checked before buying. Electricity use should be reduced wherever possible because electricity generation often involves burning fossil fuels.
Electronic devices should be unplugged when not in use. Energy-efficient LED lights should replace traditional bulbs. Reuse and recycling should be encouraged to reduce waste and pollution.
Conclusion
The greenhouse effect is a natural and necessary process that makes life on Earth possible. However, human activities have increased greenhouse gases to dangerous levels, causing global warming and climate change. The example of Venus shows how harmful a runaway greenhouse effect can be.
Protecting the Earth is our shared responsibility. Even small actions, when taken by millions of people, can make a big difference. By reducing emissions, saving energy, using renewable resources, and respecting nature, we can protect our planet for future generations. The Earth is our only home, and it is our duty to keep it safe, balanced, and livable.
