Photosynthesis: Process, Stages, Types and Role
When we were children and heard that plants are living things just like humans, many of us felt surprised. This is because plants do not walk, run, or move like animals or humans. Even then, plants show many features that make them living organisms. They breathe, respond to their surroundings, reproduce, grow, and most importantly, they make their own food. Plants and trees are truly hardworking because they prepare food not only for themselves but also for almost all living organisms on Earth.
The food made by plants is not used only for their own growth and survival. Humans and other animals also depend on this food for energy and nutrients, either directly or indirectly. The process by which plants make their food is called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is one of the most important biological processes on Earth. Without it, life as we know it would not be possible. To understand why photosynthesis is so important, it is necessary to know how it works, what it needs, its stages, types, and the factors that affect it.
What Is Photosynthesis?
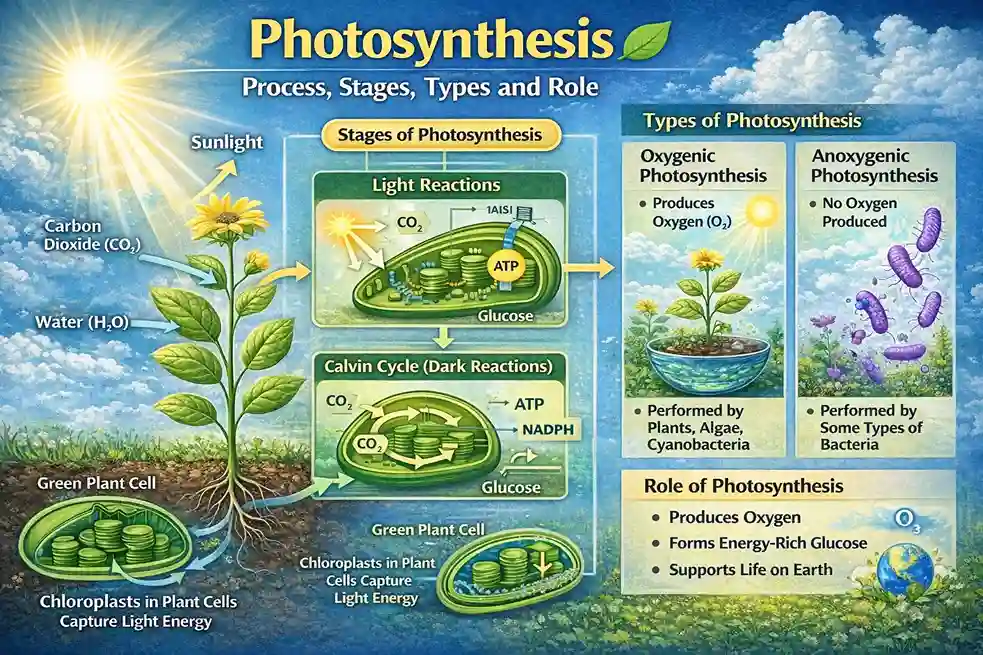
The word photosynthesis comes from two Greek words. “Photo” means light, and “synthesis” means to put together. Photosynthesis is a photochemical process, which means it is a chemical reaction that involves light. In this process, green plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
During photosynthesis, light energy from the sun is changed into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a by-product. This oxygen is essential for breathing in humans and animals. Plants use the glucose they make as food to grow, repair tissues, and produce seeds. Extra glucose is stored for later use.
Importance of Photosynthesis for Life on Earth
Photosynthesis is the base of almost all food chains on Earth. Plants are called producers because they produce food. When herbivores eat plants, they get energy stored in plant food. When carnivores eat herbivores, that energy is passed on to them. In this way, energy flows through the ecosystem.
Without photosynthesis, plants would not be able to make food. Without plants, animals and humans would not survive. Also, without photosynthesis, oxygen would not be released into the atmosphere, making life impossible for oxygen-breathing organisms. This shows that photosynthesis is essential not only for plants but for all living organisms.
Requirements for Photosynthesis
For photosynthesis to take place, plants need four main things: sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll. This process happens inside a part of the plant cell called the chloroplast. Chloroplasts are mostly found in the leaves of plants.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present inside chloroplasts. It gives plants their green color and helps in absorbing sunlight. Water is absorbed from the soil by plant roots and transported to the leaves through special tubes called xylem vessels. These vessels carry water and minerals from roots to leaves.
Carbon dioxide comes from the air. It enters the plant through tiny openings on the lower surface of leaves called stomata. These stomata also help in releasing oxygen into the air. When all these materials are available, photosynthesis can occur smoothly.
The Photosynthesis Reaction
In photosynthesis, six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water, in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, are converted into one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. Some water is also formed during this process.
The glucose produced is used by plants as food. A part of it is used immediately for energy, while the rest is stored as starch. Oxygen is partly used by plants for respiration, and the remaining oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in two main stages: the light-dependent reaction and the light-independent reaction.
Light-Dependent Reaction
The light-dependent reaction, also called the light reaction, occurs in the presence of sunlight. It takes place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast, which are arranged in structures called grana.
In this stage, light energy from the sun is captured by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Water molecules are split during this process, releasing oxygen as a waste product. This is the stage where oxygen is produced and released into the air.
Light-Independent Reaction
The light-independent reaction is also known as the dark reaction or the Calvin cycle. This stage does not need direct sunlight, but it depends on the energy produced during the light reaction. It takes place in the stroma, which is the inner space of the chloroplast.
In this stage, carbon dioxide collected from the air is combined with hydrogen using the energy from ATP and NADPH to form glucose. This glucose is the final food made by plants. Although it is called a dark reaction, it usually happens during the daytime because it depends on products of the light reaction.
Types of Photosynthesis
There are three main types of photosynthesis: C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis. All three types use the Calvin cycle, but they differ in the way carbon dioxide is fixed.
C3 Photosynthesis
C3 photosynthesis is the most common type and occurs in most plants such as wheat, rice, cotton, potatoes, and soybeans. In this process, the first stable product formed is a three-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglyceric acid. Because of this, it is called C3 photosynthesis.
C4 Photosynthesis
C4 photosynthesis is found in plants like sugarcane, maize, and sorghum. These plants usually grow in hot and dry regions. In this process, the first product formed is a four-carbon compound called oxaloacetic acid. C4 plants are more efficient in hot climates because they reduce water loss and increase photosynthesis efficiency.
CAM Photosynthesis
CAM photosynthesis is found in plants like cactus and pineapple that grow in very hot and dry conditions. CAM plants open their stomata at night to absorb carbon dioxide and store it. During the day, the stomata remain closed to prevent water loss, and stored carbon dioxide is used to make food using sunlight. This adaptation helps plants survive in extreme environments.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Several factors affect the rate of photosynthesis. Light intensity plays an important role. More light generally increases the rate of photosynthesis, while low light reduces it. Carbon dioxide concentration also affects photosynthesis. Higher levels of carbon dioxide can increase the rate up to a certain limit.
Temperature is another important factor. Photosynthesis works best between 25 to 35 degrees Celsius. Water availability is also crucial because water helps keep stomata open and supports chemical reactions. Minerals like magnesium, manganese, copper, chlorine, and phosphorus are also required for photosynthesis.
Human Impact on Photosynthesis
Human activities such as pollution, deforestation, and industrial waste are negatively affecting photosynthesis. Pollution reduces air, water, and soil quality, making it difficult for plants to absorb water and nutrients. This disturbs the photosynthesis process and creates a serious threat to life on Earth.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is one of the most important natural processes on Earth. It allows plants to make food, supports all food chains, and provides oxygen needed for life. Plants do not only think about their own survival but also support all living organisms silently. Understanding photosynthesis helps us realize the importance of plants and the need to protect them. By caring for plants and the environment, we can help maintain balance in nature and ensure a healthy future for all living beings.
